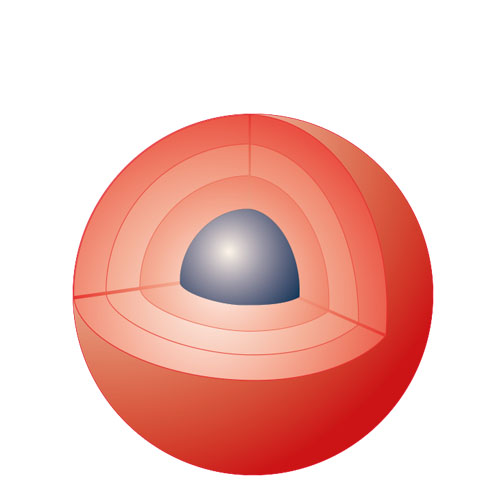
Layering of Active Substances
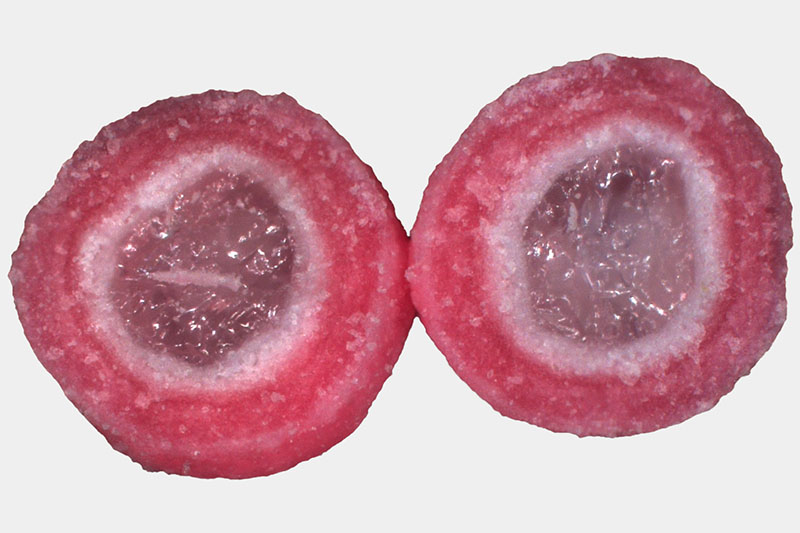
Compact, round pellets from the fluid bed.
High active ingredient content.
Perfect template for subsequent coating.
Rapid application of large layer thicknesses with a high active ingredient content to prelaid starting cores
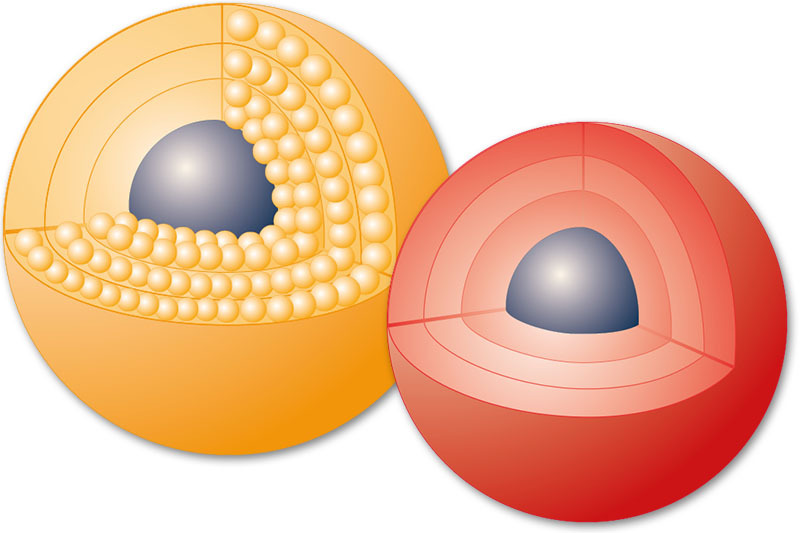
Fluidized bed processes for active ingredient layering allow large layer thicknesses to be applied to prelaid starting cores, resulting in pelltes with a high active ingredient content.
The starting material can be a starting grain or a pellet. By adding the layering substance, the pellets are built up layer by layer to the desired particle size. Pellets have excellent flowability and are easy to dose. The round shape is optimal for subsequent uniform coating, for example for retardation or controlled release.
In layering, the active ingredient can be sprayed either
- sprayed as a solution or suspension, or
- in powder form in combination with a solvent and binder.
Processes for active material layering in fluidized bed plants can be carried out in batch mode. For feasibility tests on these processes, our laboratory plant ProCell® LabSystem with rotor insert is available in our Technology Center.
Product properties of pellets by means of fluid bed active material layering at a glance:
Large
Layer Thicknesses
High
Active Ingredient Content
Dense,
Compact Structure
Mechanical
Strength
Good
Flow Behavior
Good
Dosability
Round
Pellets
Perfect
for Coatings
Multi-Layering for Different Active Substances
Powder is mixed and moistened in the fluidized bed rotor. The addition of solvent or binder takes place tangentially in the fluid bed rotor. The powder bed is set in centrifugal motion by the rotor. The process air, which is guided through a variable air gap along the edge of the rotor disk, causes a spiral movement of the powder bed.
The rotor process allows very thick film layers to be applied. The weight increase during layering can be up to 10 times the starting weight.
As in direct pelletizing, agglomerates are formed which round out into uniform and dense pellets due to the rotation of the rotor disc. The rotational speed has a direct influence on the density and size of the pellets. The moist pellets are dried either directly in the rotor (GPCG series with rotor insert) during a drying phase with higher supply air temperature or in a fluid bed dryer of the WST/WSG series. For applications with organic solvents, the plants can be inerted if required.
Product examples for the active substance layering
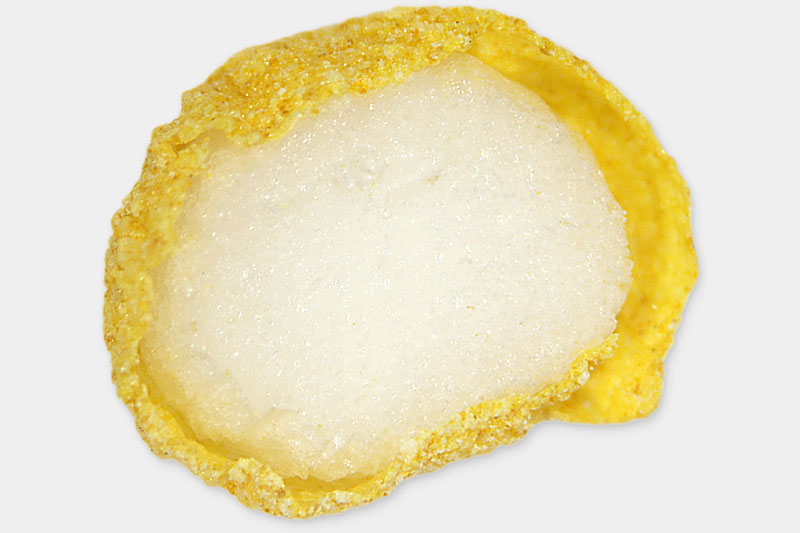
Sugar and starch, layering
Styrofoam, layering
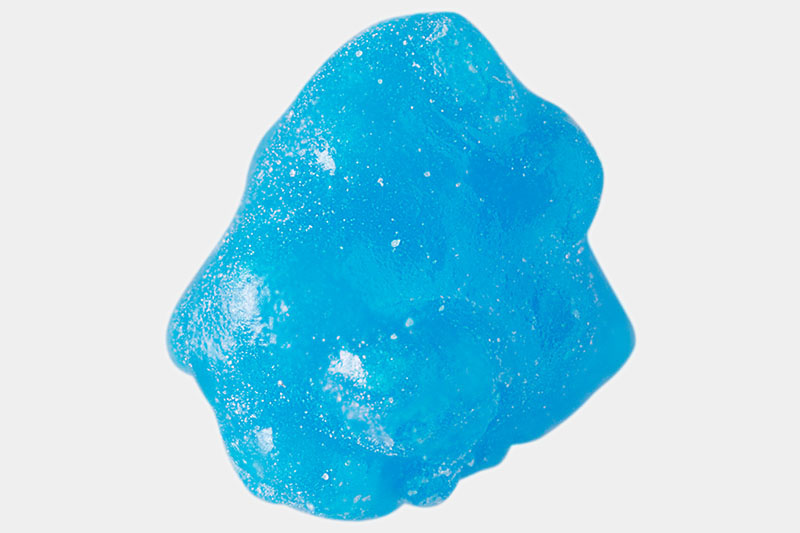
Aroma pellet, layering
Kaolin (Alumina), spray granulation + suspension layering
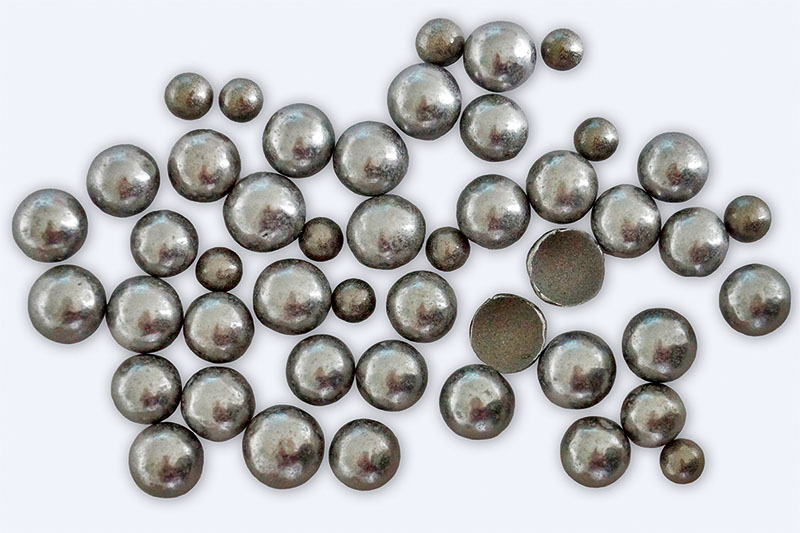
Metallic hollow spheres, suspension layering, metal powder on styrofoam core, baked out
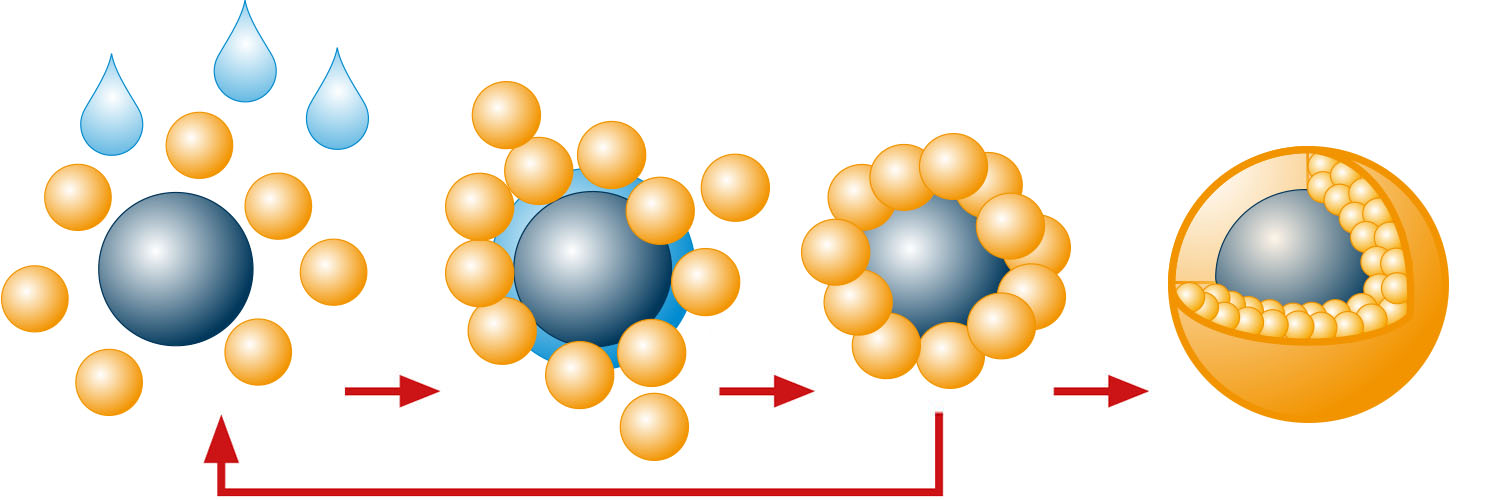
The powder layering process in detail
Pellets are produced from a powder master with the addition of a binder or solvent. The pellets are built up layer by layer to the desired particle size.
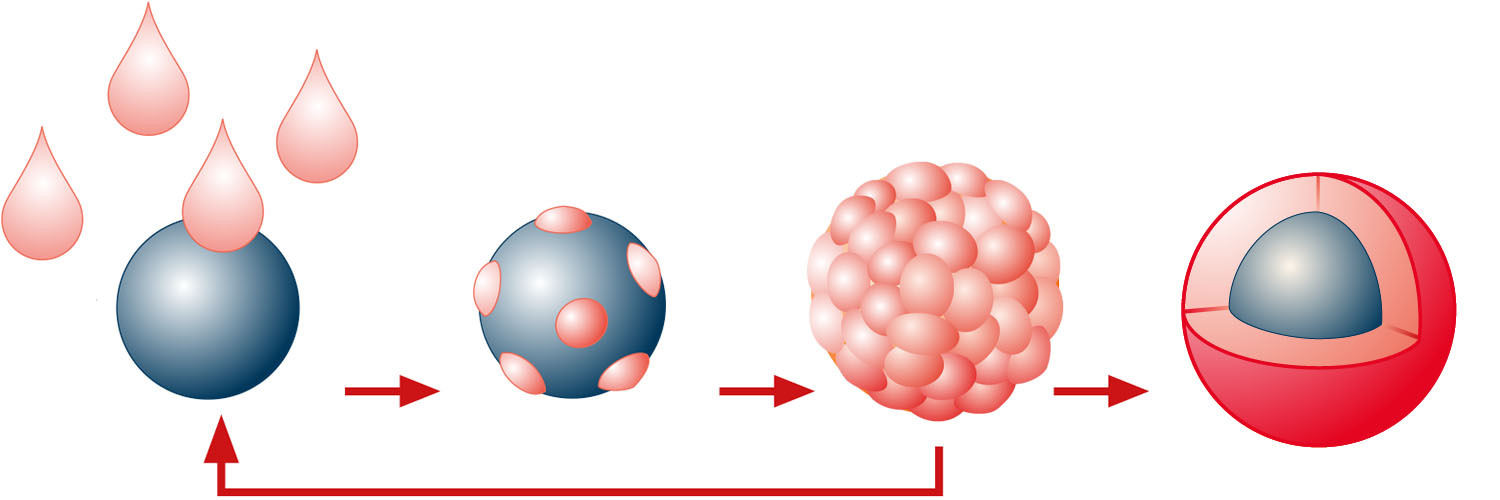
The suspension layering process in detail
Pellets are produced by spraying a solution or suspension onto a starter core. The starting material can be a starting grain or a pellet. The pellets are built up layer by layer to the desired particle size.
From the product idea to production
In our Glatt Technology Center, we provide you with access to sophisticated technologies and support in formulation, product and process development, tailored to your individual requirements. The process always starts with tests on a laboratory system. The in-house analytics laboratory enables in-process analyses to adapt particle properties to the respective application. For reliable scale-up, process and operating parameters are determined on pilot plants. Through contract manufacturing at Glatt, your new powders, pellets or granules can be manufactured, filled, packaged and delivered directly in agreed quantities. As a plant manufacturer, Glatt provides all services from project initiation, development and realization through to turnkey production in your own plant.
Further information on fluid bed and spouted bed processes can also be found in the following publications:
Published article: ‘How to Tame Recalcitrant Ingredients with Technological Processes’ PDF, English
Published article: ‘The gentle processing of highly volatile oils by fluid bed and spouted bed technology’ PDF, English
Published article: ‘Spray (micro)encapsulation of sensitive substances in matrix form – An overview of essential oil and vitamin case studies’ PDF, English
Published article: ‘Optimizing end products with finely tuned process parameters’ PDF, English
Published article: ‘Hot-melt applications for the food and beverage industry – How to safely stabilize vitamins and probiotics’ PDF, English