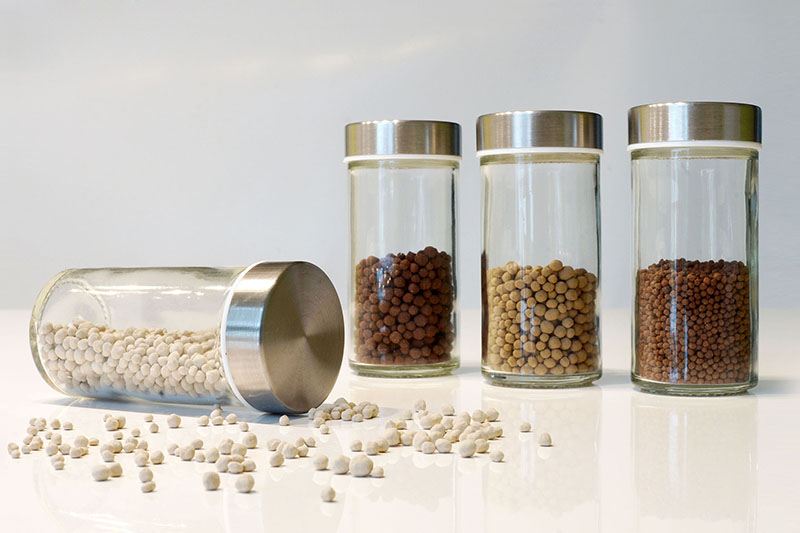
Produce abrasion-resistant, easy-to-dose, and long-term and storage-stable fertilizer granules with coordinated solubility and defined parameters such as particle size, residual moisture, and solids content.
Fertilizers – both liquid and powder – can present numerous handling challenges. Liquid solutions can be unstable and their transport can be complex in many ways. Very fine powders often behave hygroscopically and are sometimes extremely dusty. These characteristics complicate storage and application.
Fluid bed and spouted bed technologies are among the leading techniques in particle-forming processes and help overcome all these challenges. They are ideally suited for the economical production of customized fertilizers from liquids and powders. They also offer an enormous range of possibilities for optimizing the properties of fertilizers, improving their functionalization and expanding their scope of application in agriculture.
The production of fertilizer granules involves products with a pronounced depot effect and targeted delivery of the nutrient supply. Optimum dosage and the reduction of undesirable drift during transport and application require products that are abrasion-resistant, easy to dose, and stable over the long term and in storage. These properties can be perfectly adjusted by means of spray granulation in the fluid bed. Parameters such as particle size, residual moisture and solids content can be specifically influenced. You obtain homogeneous granules whose components do not segregate during transport or storage. The solubility of such granules can be very well adapted to the soil-, plant- and weather-specific conditions of use. Through suitable functionalization, the granule shape and quantity of fertilizer release into the soil can be optimally adjusted, and significantly higher product qualities can be achieved.
Homogeneous multicomponent fertilizers can be achieved particularly efficiently by the process of spray granulation in the fluidized bed. In this process, the precisely adjusted multi-component mixture is processed directly from the solution into compact granules. Granule formation and subsequent drying take place in a single process step.
This gives you porous, excellently soluble and optimally dispersible fertilizer granules as a basis for liquid fertilizers or for direct application.
Spray agglomeration in the fluid bed provides granules with a loose, porous and well-wettable structure and enables the production of highly soluble fertilizers. Spray agglomerated granules can be used as intermediates for liquid fertilizers by first converting the fertilizer solution into agglomerates for transport and storage, and then reliquefying them before application. Another interesting application is fine fertilizer agglomerates that are applied directly to plants and dissolve immediately, making them available to the plants upon contact with water. Fluidized bed spray agglomeration also improves flow behavior and eliminates negative effects such as dust formation. Fertilizer granules behave similarly to instant products: They have excellent rapid solubility and exceptionally good dispersibility. In addition, this process can prevent segregation effects of powder mixtures by combining them into agglomerates. The agglomerate structure is directly solidified during simultaneous drying. Depending on the desired properties of the raw material or the product, water or other liquid additives can be used for the granulate build-up and structure formation.
Functionalize your fertilizer granules with an optional coating for colored branding, with a coating for a pH-controlled release profile, or combine your fertilizers with active ingredients for special applications.
Functionalize your fertilizer granules with an optional coating for colored branding, with a coating for a pH-controlled release profile, or combine your fertilizers with active ingredients for special applications.
If required, the particles can then be coated with a functional protective layer to adjust further active ingredient combinations. Such a coating protects active substances, for example, from storage, transport or application-related influences, masks undesirable odors and enables colored branding as well as the targeted release of active ingredients.
Combine your seed with the required nutrient components right away. Improve germination and ultimately yield at harvest. The fertilizer granules can be coated directly with biocides, insecticides as well as fungicides or can be produced as a homogeneous mixture in the granules. Coating with biopolymers enables controlled release of the plant nutrients or pesticides.
Glatt uses its many years of experience in the production of special fertilizers to meet customer requirements such as long-term fertilization, multi-component fertilization and functionalities such as controlled release or slow release through defined coating/enveloping of the fertilizer granules. The application of various coating materials with the aid of fluid bed coating makes it possible to fulfill such functions. Through formulation development and adapted process control, completely closed coatings with low layer thicknesses can be achieved. The actual bulk material properties of the fertilizer granules remain virtually unchanged. This means that no adjustments are required in further processing or application steps.
The coating of the fertilizer granules complies with the currently valid regulations of the German Fertilizer Ordinance (DüMV) and Regulation EC No. 2019/1009. Conformity with some of these requirements is often only achieved through the use of such additives. Coating materials used in the fluid bed fertilizer coating process include: custom materials, hydrophobic materials, nitrification inhibitors, urease inhibitors, dyes, polyolefins, magnesium, polymers (sulfur-coated), biopolymers.
Customized phosphate special fertilizers and composites from phosphorus recovery with Glatt PHOS4green Technology
Planting trials were conducted as part of scientific studies to investigate the plant efficacy of different PHOS4green fertilizers in comparison with commercial fertilizer. Ryegrass (Lollium) and alfalfa (Medicago sativa) were fertilized in planters with rock phosphate, triple superphosphate, PHOS4green-P38 (double superphosphate, PHOS4green-46 (triple superphosphate) and PHOS4green Special (phosphate compound fertilizer). As a result, the amount of fresh mass harvested from triplesuperphosphate samples was comparable to that obtained when the PHOS4green fertilizers were applied, and the same was true for biomass.
Phosphorus fertilizer from sewage sludge ash – waste-free with PHOS4green
Germany was the first country in the European Union to regulate the recovery of phosphorus by law. Glatt has developed a suitable, highly efficient process in cooperation with an industrial partner and the Materials Research and Testing Institute of the Bauhaus University Weimar (MPFA): “PHOS4green” combines the recycling process with the manufacturing process for new ready-to-use, high-quality fertilizers, whereby phosphorus is first broken down from phosphate-containing sewage sludge ashes and then a ready-to-use fertilizer granulate is produced.
The “PHOS4green” technology is economical and sustainable, 100 percent waste-free and meets current market requirements for the production of ready-to-use standard and multi-component fertilizers based on recycled phosphate. In addition, the new fertilizers contain 92 percent less cadmium and about 9 percent less uranium than other recyclates (heavy metal depletion).
Superphosphate or triple phosphate, with up to 46 percent available phosphate content
Whether superphosphate, or triple phosphate, with up to 46% available phosphate content, our phosphate fertilizers meet the highest quality requirements and are particularly suitable for organic farming. As soil- and plant-specific standard fertilizers, they comply with the Fertilizer Ordinance (DüMV) and Regulation EC No. 2019/1009, are immediately marketable and can be used by farmers as usual. Fluctuations in the composition of the sewage sludge ashes are compensated for by adjusting the recipe for the suspension. This ensures consistently high quality.
Complex fertilizers (NPK, NP, PK) for customized plant nutrition
The admixture of other nutrient components in the suspension – liquid or solid – enables the production of compound fertilizers. Compound fertilizers such as NPK, NP and PK for custom plant nutrition are produced directly with the new process and applied as usual. (N component urea; K component KCl; Mg component MgCl; S component SSA; P component MAP, MKP).
With these multi-nutrient fertilizers, a needs-based and balanced fertilization is carried out, adjusted to the different nutrient requirements of the plants. This protects the environment and ensures lush growth. At the same time, leaching losses and salt damage are minimized.
There is a wide variety of process variants based on fluid bed technology or spouted bed technology. At the Glatt Technology Center in Weimar, we work with you to determine the optimum process conditions for your product in feasibility trials for product development. Various laboratory facilities and comprehensive analytical equipment are available for this purpose. On our pilot plants, we optimize the process and scale it up reliably to a stable and economical production scale. The results from this form the basis for the design and construction as well as the erection of your fluid bed or spouted bed plant, tailored to your requirements. As an alternative to our own process technology, we offer you the outsourcing of your production by means of contract manufacturing at Glatt.
Published article: A Fluid Bed Approach for Urea-based Fertilizers (Casy Study)
Urea is the leading nitrogen fertilizer worldwide. In many cases, there is a demand for special fertilizers to meet very specific requirements, for example in respect of bioavailability.
Mike Waskow, Process Engineer, Process Technology Food, Feed & Fine Chemicals, Glatt Ingenieurtechnik GmbH, Germany, explains how economical production of urea-based fertilizers can be achieved using fluidised bed technology.
» originally published in the magazine WorldFertilizer, issue 01-02.2018, Palladian Publications
Further information on this topic can also be found in the following publications:
Published article: ‘Fomulation For Success – Fluid Bed Systemes as Key for the Production of Speciality Fertilizers’ PDF, English
Published article: ‘Like a phoenix from the ashes – A recovery technology that releases phosphate from sewage sludge ashes and converts it into ready-to-use fertilizers’ PDF, English
Published article: ‘Improved performance for crop protection products’ PDF, English
Flyer A4: Glatt Functionalization of Special Fertilizers, PDF, English
Flyer A4: Glatt PHOS4green, PDF, English