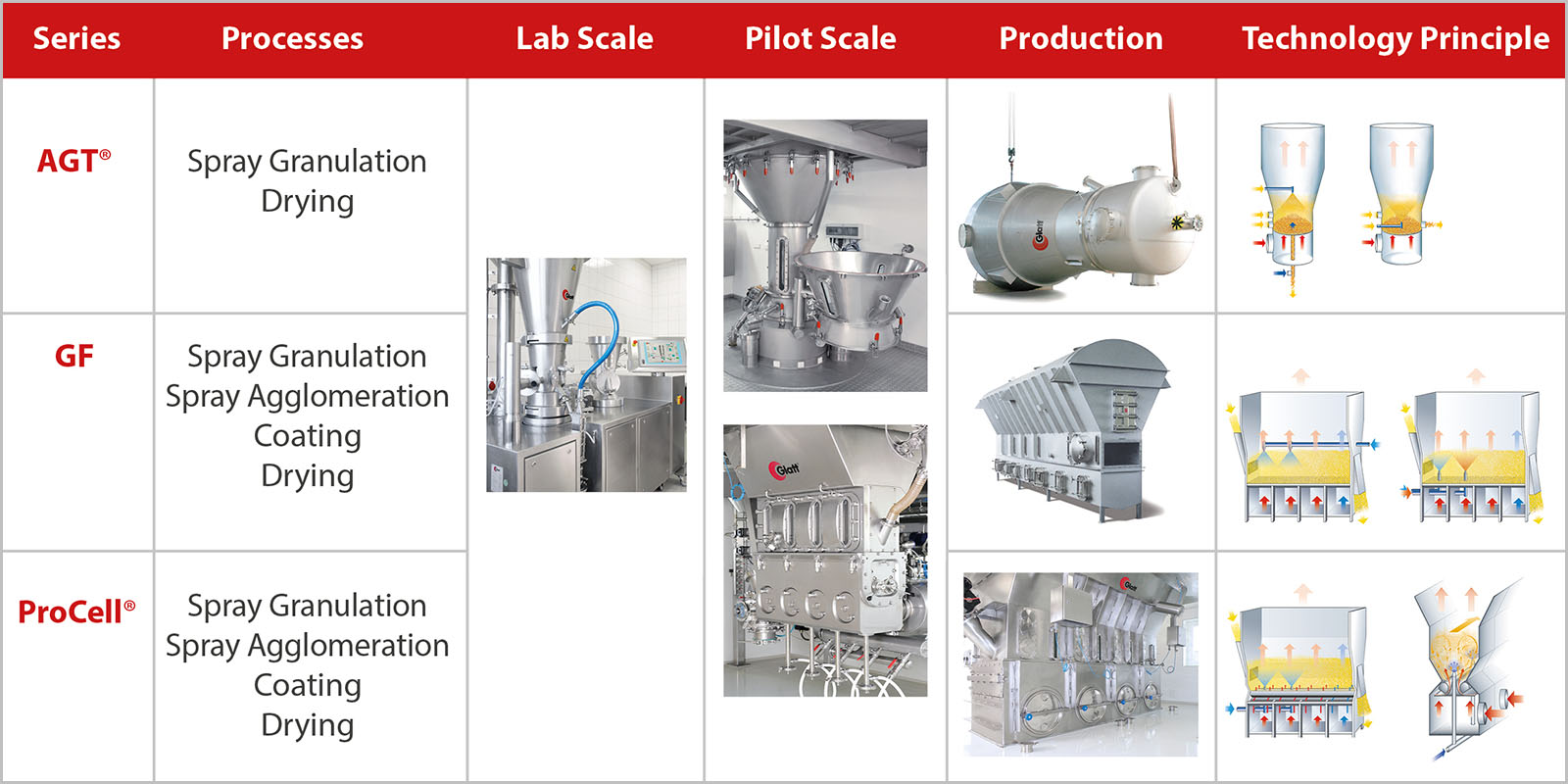
Continuous operation and batch operation
Batch by batch or continuously 24 x 7.
Glatt fluid bed and spouted bed systems can also be “hybrid”.
The decisive factors are on the one hand the raw materials, their properties and composition, and on the other hand the end product with its desired specifications.
Continuous fluid bed and spouted bed systems have been realized for forty years. Continuous granulation processes are mainly used for the production of large production quantities. Continuous operation ensures very good, reproducible product quality with extremely high efficiency, since process interruptions due to batch changes and cleaning intervals are eliminated.
Arguments in favor of batch production are small quantities, frequent product and formulation changes with thorough intermediate cleaning, limited campaign sizes, traceability or longer coating processes. Many contract manufacturers therefore usually rely on batch processes.
For innovative powder experts, the use of continuous spouted bed processes has proven to provide high efficiency even for very temperature-sensitive products. Examples of this are systems for contrast agents or for microencapsulation of food supplements and flavors. Often, one wants to produce defined starting materials for subsequent coating.
As a plant manufacturer and process expert, Glatt offers flexible plant concepts that enable various processes for particle formation and functionalization in both continuous and batch operation.
Continuously operating Glatt fluid bed systems
Arguments for continuous operation:
- economical production of large product volumes
- production volumes of more than 500 to 1000 t/a
- 24/7 shift operation
- low manpower requirements due to automation of the entire process
Glatt fluid bed systems operating in batches
Arguments for batch operation:
- production volumes below 500 to 1000 t/a
- frequent product changes
- flexible shift operation – one, two or even three shifts
- processes and handling can be flexibly adapted to customer-specific requirements
Further information on this topic can also be found in the following publications:
Published article: ‘Contract manufacturing by fluid bed and spouted bed technology: Which is better, continuous or batch process?’ PDF, English
Published article: ‘A spirit of optimism between batch and continuous production?’ PDF, German
Published article: ‘Fluid bed systems: continuous, batch or a hybrid?’ PDF, German
Published article: ‘For quick enjoyment – Fluid bed systems in batch or continuous operation’ PDF, German
Published article: ‘It’s all in the combination – Coating in the food and pharmaceutical industries, part 2’ PDF, German